Traditional SQL databases rely on a fixed schema that defines how data must be structured and stored. However, as technology evolved, rigid schema requirements became limiting for modern applications. This created the need for databases capable of ingesting diverse data types without strict constraints.
NoSQL databases address this need by allowing flexible schemas and supporting large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. They are designed for scalability, high performance, and the ability to manage rapidly changing datasets.
Four major types of NoSQL databases have emerged namely
- Document Databases
- Key-value databases
- Wide-column stores
- Graph databases
Document Databases: A document-oriented database stores data in documents similar to JSON. Each document contains pairs of fields and values.
A typical document will look like the following:{
"_id": "12345",
"name": "DBZ",
"email": "DBZ@funmail.com",
"address": {
"street": "123 fun street",
"city": "inside DB",
"state": "XXX",
"zip": "12345z"
},
"hobbies": ["music", "playing", "writing"]
}
Key-value databases: A type of NoSQL database that stores data as a key-value pair collection. They offer a simple and efficient way to store and retrieve the data, making them ideal for use cases that require fast data access. Key-value databases excel in scenarios where the primary operation is retrieving data based on a unique key.

Column family: The data is organized into columns rather than into rows. Each row can have different number of columns and columns can be added when needed.
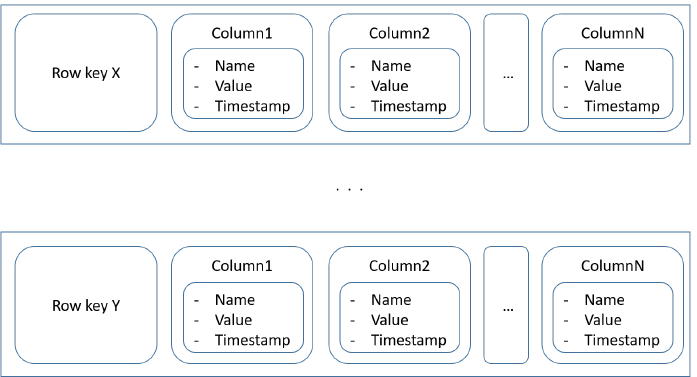
Advantages – flexibility
- Rows within a column family can have different columns.
- Add new columns to a row if we need them.
- Avoids filling with default values.
- Very fast writing / retrieving
- Scale horizontally across multiple servers.
Suitable Cases are for Content Management systems, time series data (weather, traffic..) Also in fraud-detection algorithms, recommendation engines, and catalog management.
Graph database: Graph databases store and process information using a graph data model, where data is organized as nodes (entities) and edges (relationships). This structure is similar to a Configuration Management Database (CMDB), but optimized for understanding how data points are connected rather than simply cataloging them.
Because graph databases prioritize relationships, they are ideal for applications that rely heavily on interconnected data, such as fraud detection, recommendation engines, network analysis, and social media platforms. They excel at uncovering patterns, identifying hidden connections, and performing advanced graph operations like pathfinding, centrality analysis, and real-time recommendations.
In a graph database:
Edges define the relationships between nodes—for example, FRIENDS_WITH, PURCHASED, or LOCATED_IN. Edges can also include properties and labels, allowing you to encode metadata such as timestamps, relationship strength, or interaction type.

Leave a comment