🚀 Why Does Your Website Feel Slow — Even with “Fast” Internet?
Before we deep dive into Cloud CDNs, let’s revisit two networking terms that often get confused — Bandwidth and Latency to understand CDN — and why they matter so much to user experience.
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted per second over a network connection. When we say 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1 Gbps, we’re talking about bandwidth.
Think of it as the capacity of the network — not how fast data actually reaches the user.
Latency, on the other hand, is the time delay it takes for data to travel from one point to another. It’s usually measured in milliseconds (ms).
👉 A simple analogy:
- Bandwidth is the width of a water pipe — how much water can flow at once.
- Latency is the delay between turning on the tap and water starting to flow.
Even with a very wide pipe (high bandwidth), a long delay (high latency) makes the experience feel slow.
For users, low latency = faster response, smoother interactions, and happier clicks.
🌍 Latency and Cloud Region Selection — Distance Still Matters
When deploying applications in the cloud, one of the most critical decisions is where the infrastructure lives.
Hosting services closer to users helps minimize latency — but what if:
- Users are globally distributed?
- Or they’re far from any single cloud region?
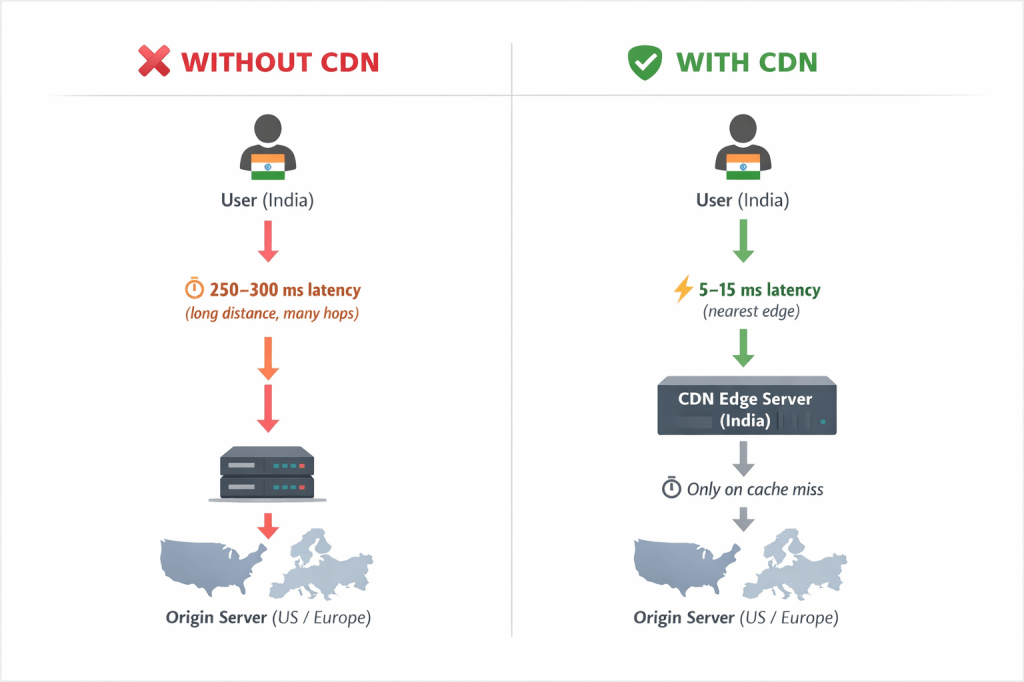
For example, if your application backend is hosted in US-Central and your users are in Mumbai, every request must travel thousands of kilometers. Each network hop adds delay — resulting in slower page loads, laggy media, and frustrated users.
And in today’s world, milliseconds matter:
⚡ Enter Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
This is where Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) changes the game.
A CDN caches copies of your content — such as HTML pages, images, videos, and static assets — across a globally distributed network of edge locations.
So when a user in Mumbai accesses your website:
- The content is served from the nearest edge location.
- Not fetched from a distant origin server.
- If the content is not there in cache, it is accessed from nearest server and copy is kept in cache for other users or for future reference.
☁️ Google Cloud CDN — Performance at the Edge
Google Cloud CDN runs on Google’s globally distributed edge network, caching content closer to users worldwide.
When integrated with a Global HTTP(S) Load Balancer:
- Requests served from the CDN cache never reach your backend
- Your infrastructure handles fewer requests
- Users experience faster, smoother, and more reliable web performance
In short, Cloud CDN turns geographical distance from a problem into a competitive advantage.
Key Takeaway
High Bandwidth ≠ Fast Experience
Low Latency + CDN = Fast Experience
Leave a comment