A trigger in DB2 is a procedural code that is automatically executed in response to specific data modification events—such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE—on a table or view. Triggers act as automated reactions to changes in data, helping enforce business rules, maintain audit trails, or synchronize data across tables.
⚙️ Key Characteristics of DB2 Triggers
- Automatic Execution: Triggers are fired automatically when the defined event occurs.
- Table-Specific: Each trigger is associated with a single table.
- Non-bypassable: Once defined, triggers cannot be skipped or disabled during normal operations.
- Granularity Control: You can define whether the trigger should execute FOR EACH ROW or FOR EACH STATEMENT.
🛠️ How to Define a Trigger in DB2
Here’s a breakdown of a sample AFTER INSERT trigger in DB2. In the example below we will insert a new value in a new table when there is an insert happened in base table. In this example, the base table is VXXX22.

The key statements are marked in sequential manner (1),(2)….(6)
(1)- Create Trigger is the key word to define and the trigger name is VXXXXIX
(2)- After Insert is the trigger activation time. So the trigger will be activated after an insertion happens on the table VXXX22(dummy name). Similar for Before Insert.
(3)- New transition variable correlation name N.
(4)- FOR EACH ROW defines the Granularity, ie the trigger will be invoked for operation on each row.
(5)- The operation to be performed when the trigger is hit. In this example we are inserting the values into another table named P.P00TXX. Consider the table contains two columns: TRANSAC_CODE and TRANSAC_TEXT. In this example the new values of the table VXXXIX are being concatenated and inserted into P00TXX table. The new values are captured as N.CUSTOMER_ADDR, N.LAND, N.CITY, N.POSTAL CODE etc.
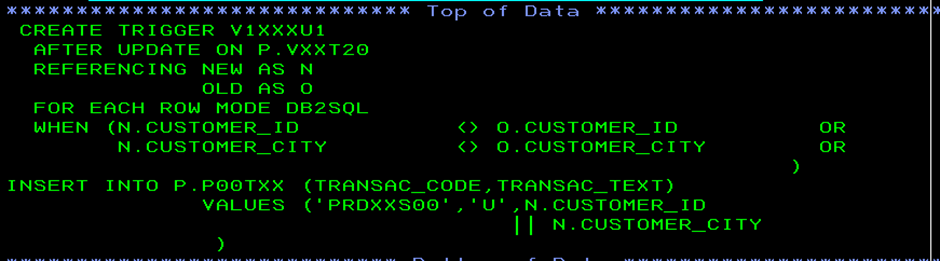
Defining an update Trigger :
The following definition can be used to check if the old and new values of the table(before and after update operation on the table) are same or not. If the new values and old values are different, the new values will be inserted into the P00TXX table or any other operation can be performed as needed.
📘 Understanding Transition Variables and Correlation Names
DB2 triggers use transition variables to reference row values before and after a data modification:
| Event Type | OLD Variable | NEW Variable |
|---|---|---|
| INSERT | N/A | NEW |
| DELETE | OLD | N/A |
| UPDATE | OLD | NEW |
These variables are accessed using correlation names like O and N.
Transition Variables and Correlation Names:
Thus to summarize the use of transition variable and correlation name:
A transition variable is a variable that references a value in the SQL for a triggered action.
Each trigger can have one NEW view of the table and one OLD view of the table, to which the trigger is attached.
When an INSERT occurs, the NEW variable contains the rows that were just inserted into the table
When a DELETE occurs, the OLD variables refers to the rows that were just deleted from the table.
For an UPDATE, the NEW and OLD contains the values of table after the update and before the update respectively.
OLD: Refers to the row values before the operation.
NEW: Refers to the row values after the operation.
Leave a comment